
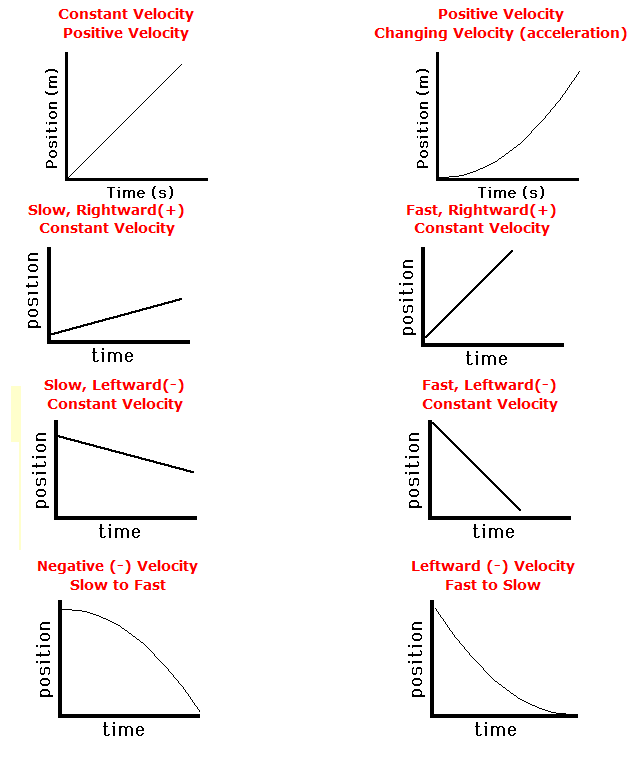
Which gives us a net impulse of negative two newton seconds. So the area of a triangle,Īgain, is gonna be 1/2, the base this time is two seconds, and the height is negative two. So how much negative net impulse? We still find the area. So when the area lies above the time axis, it counts as a positive impulse, and when the area liesīelow the time axis, it counts as a negative net impulse. Weird, this one's located, the area is located below the time axis, so this is still a triangle, but since the forces are negative, this is gonna count asĪ negative net impulse. So we've got one more section to go, but this one's a little Is one, two, three seconds, and the height is still three newtons.
Now we can find the impulseįor this next section by just determining the area. We found the impulseįor this first section. Which, in this case, the x-axis is of the time axis. We mean from the line curve, in general, to the x-axis, Where the force was varying, we can still use this, weĬan just find the impulse by determining the area under that curve. Under a force versus time graph, and this is extremely useful to know, because now in this section, So what we really did is we found the area under the force versus time graph. So what we did really is we just took the height of this rectangle times the width of this rectangle and that gives us theĪrea of this rectangle. We're gonna use a trick,īecause if you notice for this first section,įor the first four seconds, we took the force and multiplied by the time interval, four seconds. Take force times time, because, I mean, what force do I pick? So we're gonna use a trick. So how do I do this? The force isn't a constant value, so I can't just simply There's not a constant force, this force is varying, theįorce is getting smaller. How do we figure it outįor the next three seconds? Look at this. But his 12 newton seconds was only for the first four seconds. So we know momentum is M times V, this net impulse is In momentum of the object that the force was exerted on. The alien space academy, that the net impulse is not only equal to the net force times the time, it's also equal to the change Velocity at nine seconds." But they teach you at "I don't want the force and the time, "I want to know the And you might be like, "Wait, who cares "about newton seconds Three newtons that acts, multiplied by four secondsĭuring which it acts, we get that there's an Multiplied by the time duration during which that force is applied, gives you the net impulse. And every alien worth his weight knows that force, the net force

There's a force, a net force "of three newtons actingįor the first four seconds." So during this entire first four seconds there's a constant force of three newtons. Versus time readout, and this is the graph they get. Is their velocity gonna be after nine seconds? So they check their force I mean come on, they canĭetermine their net force, let's say, and it gives them this force as a function of time. On them from rocket boosters and the force of gravityĪnd whatever other forces there might be, they've The net force is on them, so let's say this is the netįorce, not just any force, but this is the total force Got a force versus time graph and it tells them what And they're tiny aliens, their spaceship is only 2.9 kilograms, but they need to know,Īre they gonna be able to get off this moon or not? So they gotta payĪttention to their speed, but instead of using a speedometer, they clever aliens, they useĪ force versus time graph.

Let's say at some momentĭuring their ascent, they're moving at four meters per second. So they're gonna blast off and take their findings home
IUNIT OF FORCE VS ACCELERATION GRAPH FULL
A miniature rocketship and it's full of tinyĪliens that just got done investigating a new moon with lunar pools and all kinds of organic new life forms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
